Welcome to our Narcissistic Self Test, a quick and insightful tool designed to help you explore and understand certain behavioral traits associated with narcissism. Narcissistic tendencies can impact various aspects of one’s life, including relationships, work, and overall well-being.

This brief self-assessment test is not a diagnostic tool, but rather a starting point for self-reflection. It aims to provide you with a view of potential narcissistic behaviors that may warrant further exploration. Remember, self-awareness is the first step towards personal growth, and this test is intended to be a supportive resource on your journey of self-discovery. Take a few moments to reflect honestly on your responses, and let this tool be a guide as you navigate the complexities of human behavior.
Am I a Narcissist or an Empath? Take our 2 minute Narcissistic Personality Disorder online test to better understand your self-image and how you relate to others.
Narcissistic Traits Quiz Test
1. When you talk about your achievements, you tend to:
2. When you win an award or honor, you:
3. If someone doesn’t notice your new clothing or haircut, you:
4. When you walk into a party where you don’t know anyone, you tend to:
5. The most important things to you are:
6. When coworkers or supervisors criticize your work, you:
7. Your reaction to a small mistake made by an employee is to:
8. Your response to a close friend’s exciting news is likely to be:
9. If you have to miss or cancel an important event or party you:
10. At work, you are most fulfilled by:
11. You post on social media:
12. When interacting with new acquaintances, you:
13. If you have to cancel plans with friends because something more prestigious or admired came up, you:
14. Your social media profiles highlight:
15. When you are irritated or upset, people close to you:
16. You are most comfortable in jobs where you are:
17. You would describe yourself as someone who:
18. Your reaction to highly successful and acclaimed friends or partners is:
19. Your approach in competitive scenarios is to:
20. Most of your close friends are:
21. When watching award shows, you:
22. If your partner or close friend achieves sudden prestige or fame, you:
23. When you make mistakes that negatively impact subordinates or teammates, you:
24. What matters to you more than most other things:
25. You openly share credit for team successes but tend to:
26. When pursuing goals and ambitions:
27. Your response when a colleague surpasses your work accomplishments is to:
28. When pursuing romantic partners, you tend to seek people who:
29. You find it easiest to empathize and connect with people who:
30. Feedback from bosses and mentors tends to be:
Your Narcissistic Traits:
Results of your Narcissistic Personality Quiz:
No Narcissism: 20%
Mild Narcissism: (21% – 50%)
Narcissistic Traits: (51% – 70%)
Complete Narcissism: (70%+)
Note: It’s important to note that self-diagnosing or diagnosing others based on a set of questions may not provide an accurate assessment of narcissism or any other psychological condition. This Quiz Test is just for Awareness purposes.
Most Common Narcissistic Traits:
All people have some narcissistic traits—it’s part of human nature to want attention and validation. But a small slice take it to the extreme, unable to relate to others as fully realized human beings. Their inflated sense of self both shields and torments them, driving them to constantly seek the praise and power they feel entitled to. Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD) is not very common. It only impacts a small percentage of the general population, estimated to be between 0.5% and 1%. This means that out of 100 people, only around half a person to one person might be diagnosed with NPD.
Historical Narcissistic Personalities?
Examples of historical figures often cited for displaying narcissistic traits include political leaders, such as Adolf Hitler and Joseph Stalin, and business magnates, such as Howard Hughes.
What is Narcissistic Personality Disorder or NPD?
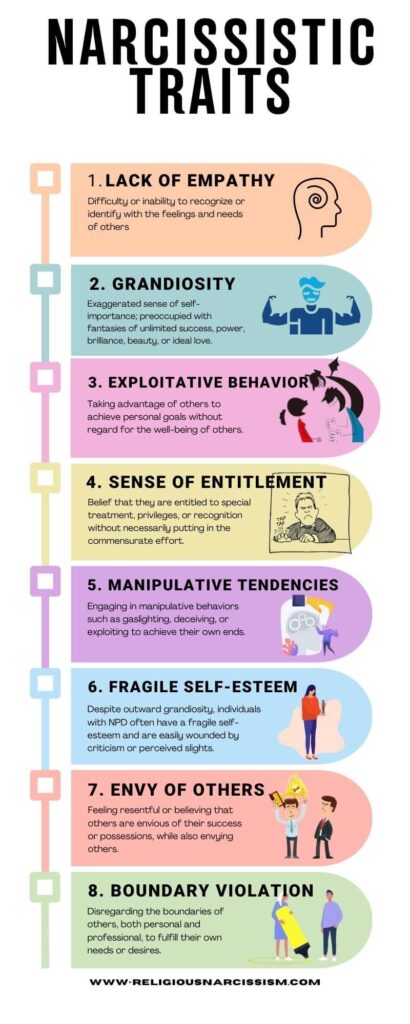
Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD) is a psychological condition characterized by a pervasive pattern of grandiosity, a constant need for admiration, and a lack of empathy for others. Here are some key facts about narcissistic individuals based on credible research sources:
Prevalence:
- According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), NPD has a prevalence of around 6.2% in the general population.
- It is more commonly diagnosed in males than females.
Etiology:
- The exact causes of NPD are not fully understood, but a combination of genetic, neurobiological, and environmental factors is believed to contribute.
- Childhood experiences, such as excessive praise or insufficient criticism, may play a role in the development of narcissistic traits.
Characteristics:
- Narcissistic individuals often exhibit a sense of entitlement, believing that they deserve special treatment and admiration.
- They may engage in fantasies of unlimited success, power, brilliance, or beauty.
- Lack of empathy is a hallmark trait, making it difficult for them to understand or connect with the feelings and needs of others.
Relationships:
- Narcissists may have difficulty maintaining healthy relationships due to their self-centeredness and inability to empathize with others.
- They may exploit others to achieve their own goals and may struggle with genuine emotional intimacy.
Comorbidity:
- NPD is often comorbid with other mental health disorders, such as depression, anxiety, and substance abuse.
- Co-occurring personality disorders, like borderline personality disorder, may also be present.
Challenges in Treatment:
- Narcissistic individuals may be resistant to seeking treatment as they may not perceive themselves as having a problem.
- Psychotherapy, particularly approaches such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and psychodynamic therapy, is often recommended, but treatment can be challenging.
Impact on Work and Social Life:
- While narcissistic individuals may achieve success in their careers due to their ambition and self-confidence, their interpersonal difficulties can create challenges in the workplace.
- In social settings, their need for constant admiration may lead to strained relationships.
Development of Narcissism Tests
The most widely used measure of narcissism is the Narcissistic Personality Inventory (NPI) developed by Raskin and Hall in 1979. To create the NPI, Raskin and Hall constructed over 200 items describing narcissistic traits. After multiple validation tests, they narrowed it down to the current 40-item forced-choice version.
The NPI measures narcissism as a continuous dimension in the general population, not just as a clinical disorder. Scores range from 0 to 40, with higher scores indicating more severe narcissistic tendencies. The NPI assesses facets like authority, self-sufficiency, superiority, exhibitionism, exploitativeness, vanity, and entitlement.
Other narcissism assessments have been validated against the NPI, like the Pathological Narcissism Inventory (PNI). This evaluates more pathological elements of narcissism in terms of contingencies like shame, hiding the self, and devaluation. The Five-Factor Narcissism Inventory (FFNI) measures narcissism through five dimensions: antagonism, neuroticism, conscientiousness, extraversion, and openness.
Comparing Different Narcissism Tests
The NPI remains the standard measure of narcissism in social psychology. It best evaluates narcissism as a personality dimension in the general population. The PNI and HSNS (Hypersensitive Narcissism Scale) are more clinically focused in assessing pathological narcissism in ways directly connected to NPD.
The type of narcissism test used depends on the purpose – whether exploring the role of narcissism in relationships, evaluating clinical symptoms, or conducting personality research. The NPI is best for broader research on narcissism’s general interpersonal effects. The PNI and HSNS address the inner experience of narcissists. And tools like the FFNI evaluate interactions between narcissism and other major personality domains. Being clear about whether pathological vs. grandiose narcissism is being measured allows proper test selection.
Narcissistic Personality Disorder FAQs:
What are the common signs and symptoms of NPD?
Common signs include an exaggerated sense of self-importance, fantasies of unlimited success, a belief in one's uniqueness, a constant need for excessive admiration, and a lack of empathy.
What causes Narcissistic Personality Disorder?
The exact causes are not fully understood, but a combination of genetic, neurobiological, and environmental factors, as well as childhood experiences, may contribute to the development of NPD.
Can narcissistic traits be present without a diagnosis of NPD?
Yes, narcissistic traits exist on a spectrum, and not everyone with these traits meets the criteria for a formal diagnosis of NPD.
How is NPD diagnosed?
A qualified mental health professional, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist, typically diagnoses NPD through a comprehensive assessment of an individual's symptoms, behavior, and history.
Is there effective treatment for Narcissistic Personality Disorder?
Psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or psychodynamic therapy, is often recommended. However, treatment can be challenging due to the individual's resistance to acknowledging the need for change.
Can someone with NPD have successful relationships?
Individuals with NPD may struggle in relationships due to their self-centeredness and lack of empathy. Successful relationships may be possible with therapy and a willingness to address and manage the symptoms.
Do people with NPD realize they have a problem?
Many individuals with NPD may not recognize their own problematic behaviors, as they often have a grandiose self-perception. This lack of insight can make it challenging to convince them to seek help.
Are there any comorbid conditions associated with NPD?
NPD is often comorbid with other mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety, and substance abuse. It may also co-occur with other personality disorders.
Can NPD be managed or cured?
While there is no cure for NPD, individuals can learn to manage their symptoms through therapy and develop healthier ways of relating to others. Long-term improvement often requires ongoing self-awareness and commitment to change.
Helpful Resources:
- APA Dictionary of Psychology
- https://mydr.com.au/mental-health/narcissistic-personality-disorder-npd/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Narcissism
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5-TR
- THE ENCYCLOPEDIA OF WORLD PROBLEMS & HUMAN POTENTIAL
- https://deepblue.lib.umich.edu/bitstream/handle/2027.42/57606/skonrath_2.pdf
- https://www.latimes.com/archives/la-xpm-2011-jan-06-la-oe-daum-narcissism-20110106-story.html
- Narcissistic Personality Disorder in Clinical Health Psychology Practice
- Narcissism Driven by Insecurity, Not Grandiose Sense of Self
- Current understanding of narcissism and narcissistic personality disorder
- Running Head: Narcissistic Personality Disorder by LWTech.edu
